Simple Program
Make a directory named new in C:\ for Windows open a cmd
$ cd C:\new
If on Linux Open a terminal and run the following command:
$ mkdir $HOME/new
-
Then launch the Notepad or any other Text Editor and paste the following code:
class Simple { public static void main(String args[]){ System.out.println("Hello World"); } } -
Save this file as Simple.java in
newdirectory.
Open a terminal and run the following command:
-- Windows
javac Simple.java
-- Linux
javac $HOME/new/Simple.java
It will produce .class file in new directory now execute the program
-- Windows
java -cp C:\new\ Simple
-- Linux
java -cp $HOME/new/ Simple
output: Hello World
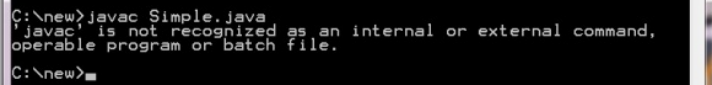
Troubleshooting:
javac is not recognized as an internal or external command
Solution: Set Proper Path
Let’s understand our first Java program
Let’s see what is the meaning of class, public, static, void, main, String[], System.out.println().
class keyword is used to declare a class in Java.
public keyword is an access modifier which represents visibility, it means it is visible to all.
static is a keyword, if we declare any method as static, it is known as static method. The core advantage of static method is that there is no need to create object to invoke the static method. The main method is executed by the JVM, so it doesn’t require to create object to invoke the main method. So it saves memory.
void is the return type of the method, it means it doesn’t return any value.
main represents startup of the program.
String[] args is an array used for command line arguments.
System.out.println() is used print statement.
Internal Details of Hello World Program
On previous page Java Virtual machine, we have learnt about the Java code Compilation and Execution in Java VM. Here, we will see the example of that how it work at compile time and runtime.
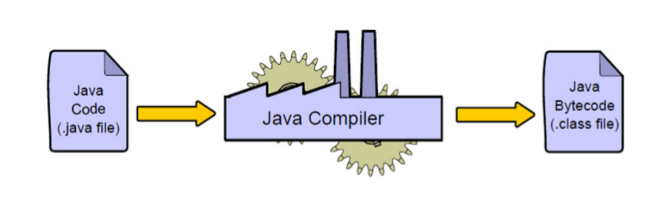
Compile Time
Java file is compiled by Java Compiler (which doesn’t interact with OS) and converts the Java (Human Readable) code into (Type of Machine Code) bytecode.
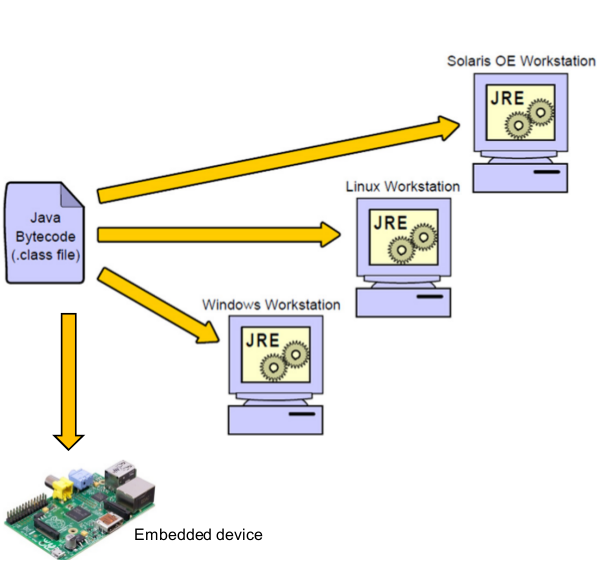
Runtime
Class file is loaded by JVM (which interact with OS) and converts the Bytecode into Machine Code.
- Classloader: is the subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files.
- Bytecode Verifier: checks the code fragments for illegal code that can violate access right to objects.
- Interpreter: read bytecode stream then execute the instructions.
Saving Java source file other than the class name
If the class is not public
You can save file with other name but, have to compile it by file name and execute it by class name.
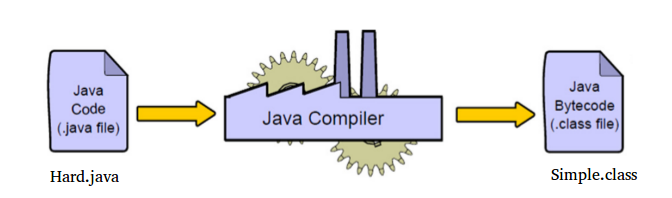
Lets save the above Simple Java program file name as Hard.java.
- Now Compile the Hard.java
If the class is public
public class A {}Lets save the above public A class Java program file name as B.java.
- Now Compile the B.java
$ javac B.java
When saving Java source file with public class access modifier so it will gives compile time error below:
error: class A is public, should be declared in a file named A.java public class A {}
Having Multiple Classes in Java source file
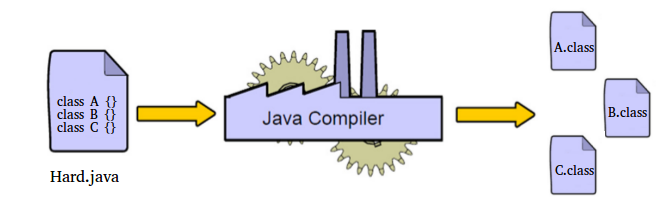
class A {}
class B {}
class C {}Open terminal and run the following command:
javac Hard.java
java -cp . A
java -cp . B
java -cp . Ccp refers to classpath and
. refers for the standing location on terminal.Continue
Proceed to Lab 1 - Java Comments.