Principles
Visit Primary Goals in your web browser.
- It must be “simple, object-oriented, and familiar”.
- It must be “robust and secure”.
- It must be “architecture-neutral and portable”.
- It must execute with “high performance”.
- It must be “interpreted, threaded, and dynamic”.
Key Features of Java
These are the key features for Java Principles.

1) Simple
According to Sun, Java language is simple because:
-
syntax is based on C++ (so easier for programmers to learn it after C++) removed many confusing and/or rarely-used features e.g.
-
Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance, no pointers in Java, and no pass by reference in Java.
-
No need to remove unreferenced objects because there is Automatic Garbage Collection in Java.
-
2) Object-Oriented
Object-oriented means we organize our software as a combination of different types of objects that incorporates both data and behaviour.
Basic concepts of OOPs are:
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
We will discuss these in detail later.
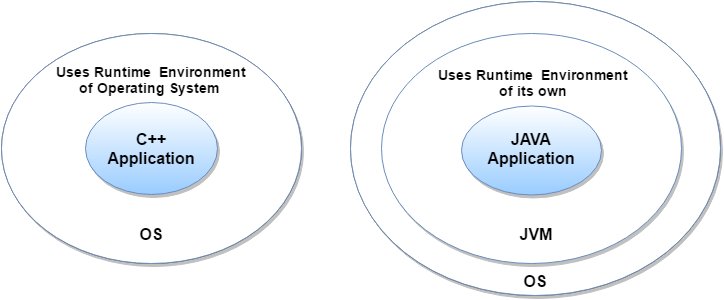
3) Platform Independence
- Java source code is stored as text in a .java file.
- The .java file is compiled into .class files.
- A .class file contains Java bytecodes (instructions).
- The bytecodes are interpreted at run time.
- The Java .class file is the executable code.
They call it WORA (Write Once and Run Anywhere)
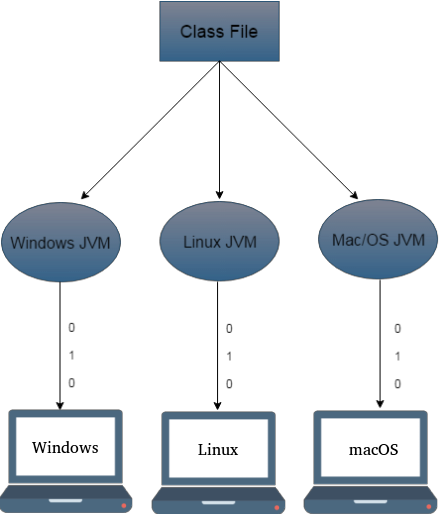
Java code can be run on multiple platforms because bytecode is a platform-independent code. e.g. Windows, Linux, Sun Solaris, Mac/OS etc.
4) Secured
- No explicit pointer.
- Java Programs run inside virtual machine sandbox.
- Classloader: adds security by separating the package for the classes of the local file system from those that are imported from network sources.
- Bytecode Verifier: checks the code fragments for illegal code that can violate access right to objects.
- Security Manager: determines what resources a class can access such as reading and writing to the local disk.
5) Robust
Robust simply means strong. Java uses strong memory management. There are lack of pointers that avoids security problem. There is automatic garbage collection in Java. There is exception handling and type checking mechanism in Java. All these points makes Java robust.
6) Architecture-neutral
There is no implementation dependent features e.g. size of primitive types is fixed. In C programming, int data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. But in Java, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32 and 64 bit architectures.
7) Portable
We may carry the Java bytecode to any platform.
8) High-performance
Java is faster than traditional interpretation since byte code is “close” to native code still some slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++)
9) Distributed
We can create distributed applications in Java. RMI and EJB are used for creating distributed applications. We may access files by calling the methods from any machine on the internet.
10) Multi-threaded
A thread is like a separate program, executing concurrently. We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. The main advantage of multithreading is that it doesn’t occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area. Threads are important for multimedia, Web applications etc.
Continue
Proceed to Java Virtual Machine.