Lets consider a Java program
It can be defined as a collection of objects that communicate via invoking each other’s methods. Let us now briefly look into what do class, object, methods, and variables mean.
Class
A class can be defined as a template or blueprint that describes the behavior and state of an object. It can contain variables, operations, methods and other properties for an object.
A Object: have states and behaviors.
Syntax:
class NameofClass {
// class body
}Methods
A method is basically a behavior. A class can contain many methods. It is in methods where the logics are written, data is manipulated and all the actions are executed.
Syntax:
accessModifier returnType nameOfMethod (params or args) {
// method body
}accessModifier − It defines the access type of the method and it is optional to use.
returnType − Method may return a value.
nameOfMethod − This is the method name. The method signature consists of the method name and the parameter list.
params or args − The input parameters, the number of declared variables for a method. Method may contain no parameters.
method body − The method body contains the list of statements which has to be execute.
Example:
public void methodName (int a) { // method block start
// method body
}// method block endCalling of a Method
methodname(args); //calling method with args
methodname(); //calling method which have no args
Variables
A variable is data member of a class, each object has its unique set of variables. A variable stores a value having a type which known as it’s data type and variable also called a container having not fixed values.
The constants are used instead of variables to store fixed values.
Syntax:
class className{
type variableName; // data member
}Example:
class A{
int a; // data member
}Java Identifiers
All Java components require names. Names used for classes, variables, and methods are called identifiers.
In Java, there are several points to remember about identifiers. They are as follows −
- All identifiers should begin with a letter (A to Z or a to z), currency character ($) or an underscore (_).
- After the first character, identifiers can have any combination of characters.
- A key word cannot be used as an identifier.
- Most importantly, identifiers are case sensitive.
Examples
legal identifiers: age, $salary, _value, __1_value.
illegal identifiers: 123abc, -salary.
Reserved Keywords

Reserved keywords cannot be used as an identifiers such as the name of a variable, function, or label.
Java Naming conventions
By using standard Java naming conventions, you make your code easier to read for yourself and for other programmers. Readability of Java program is very important. It indicates that less time is spent to figure out what the code does.
Java follows camelcase syntax for naming the class, interface, method and variable.

Method Signatures
How many ways to write a Java program
1) By changing sequence of the access modifier.
Let’s see the simple code of main method.
static public void main(String args[])2) subscript notation [] in Java can be used with type, before or after variable name.
Let’s see the different codes to write the main method.
public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String []args)
public static void main(String args[])3) You can provide var args support to main method by replacing subscript notation with 3 ellipses (dots).
Let’s see the simple code of using varargs in main method.
public static void main(String... args)4) Semicolon at the end of class in Java is optional.
-
Let’s see the simple code.
class Simple { public static void main(String args[]){ System.out.println("Hello World"); } };
Java Valid or Invalid Method Signatures
- valid main method signature
public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String []args)
public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String... args)
static public void main(String[] args)
public static final void main(String[] args)
final public static void main(String[] args)
final strictfp public static void main(String[] args)- invalid main method signature
public void main(String[] args)
static void main(String[] args)
public void static main(String[] args)
abstract public static void main(String[] args)Unicode System
Java use Unicode System, Unicode is a universal international standard character encoding that is capable of representing most of the world’s written languages.
Before Unicode, there were many language standards:
- ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) for the United States.
- ISO 8859-1 for Western European Language.
- KOI-8 for Russian.
- GB18030 and BIG-5 for chinese, and so on.
This caused two problems:
A particular code value corresponds to different letters in the various language standards.
The encodings for languages with large character sets have variable length. Some common characters are encoded as single bytes, other require two or more byte.
To solve these problems, a new language standard was developed i.e. Unicode System.
In unicode, character holds 2 byte, so Java also uses 2 byte for characters.
- lowest value: \u0000
- highest value: \uFFFF
Special Characters
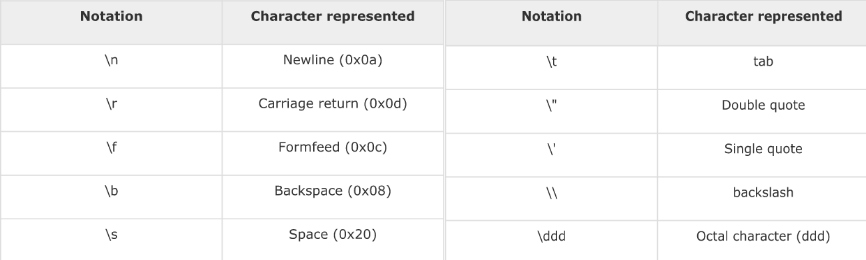
Continue
We will be looking into more details in the next sections.
Proceed to Chap 1 - Java Variables.