In this section, you will learn how to use operators and the rules of precedence.
Operators in Java
Operators are mainly symbols that is used to perform operations between two or more operands.
e.g: + - * /
We can divide Java operators into the following groups.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Misc Operators
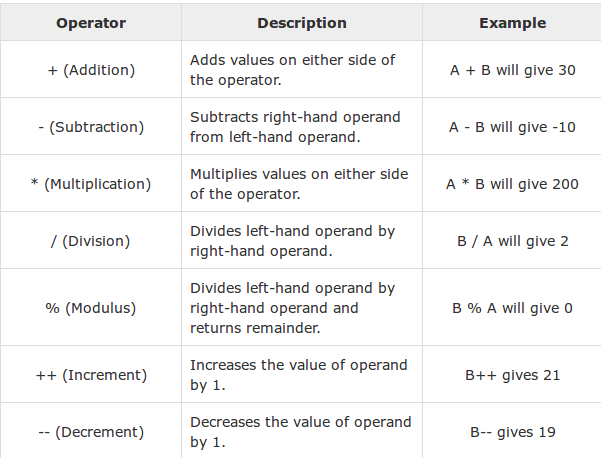
The Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used in mathematical expressions in the same way that they are used in algebra. The following table lists the arithmetic operators
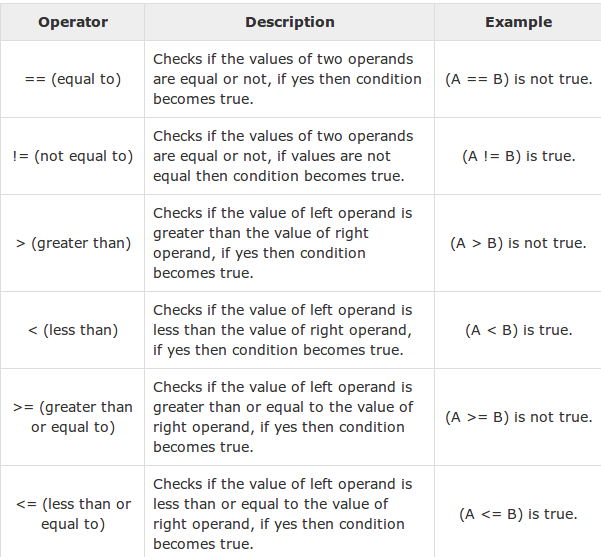
The Relational Operators
The Bitwise Operators
Bitwise Operators which can be applied to the integer types, long, int, short, char, and byte.
Bitwise operator works on bits and performs bit-by-bit operation.
Assume if a = 60 and b = 13 now in binary format they will be as follows
a = 0011 1100
b = 0000 1101
a&b = 0000 1100
a|b = 0011 1101
a^b = 0011 0001
~a = 1100 0011

The Logical Operators

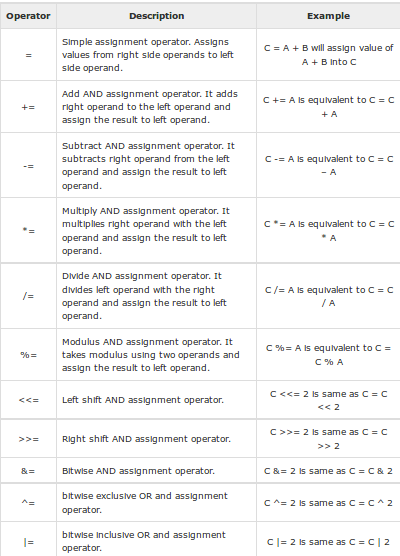
The Assignment Operators
The Misc Operators
There are few other operators supported by Java Language.
Conditional Operator ( ? : )
Conditional operator is also known as the ternary operator. This operator consists of three operands and is used to evaluate Boolean expressions.
The goal of the operator is to decide, which value should be assigned to the variable. The operator is written as −
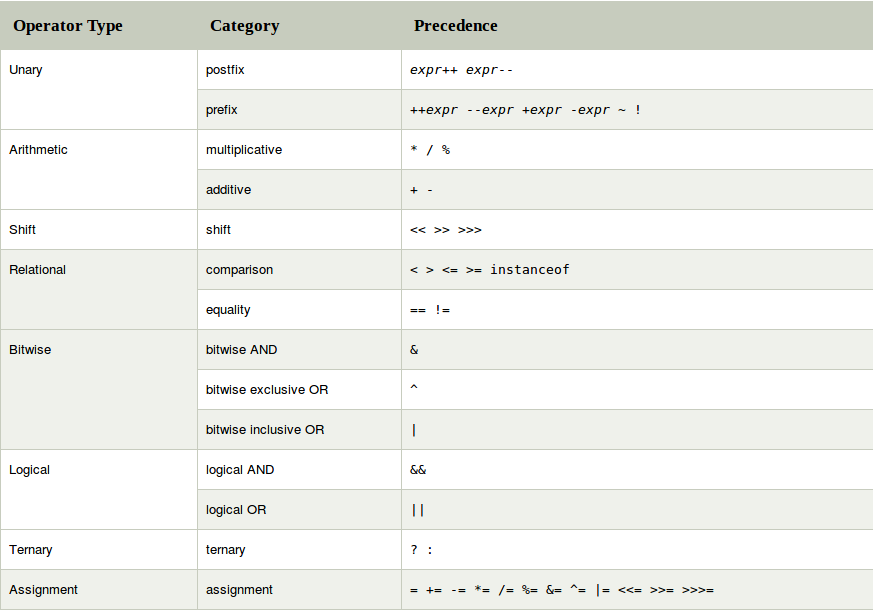
variable x = (expression) ? value if true : value if falseJava Operator Precedence
Continue
Proceed to Chap 1 - What is Method ?.